Ackie monitors (or spiny tailed monitors) make a good first monitor lizard or a step up from the more commonly kept agamid lizards such as bearded dragons.

Like bearded dragons, Ackies are from the dryer regions of Australia and need similar (but not the same) conditions. They get a little larger (well longer at least) and so will need a large enclosure. They should also be quite active, making a larger enclosure essential.
Due to their relatively small size (for monitors) and generally good temperment, Ackies make a good starter monitor but are attractive enough to appeal to more experienced keepers too.
Enclosure
Akies get to around 2 feet in length (males slightly larger). They are a very active lizard and like to burrow in the substrate. This, coupled to the fact that they like it very hot in the basking area (50-60 degrees centigrade) means that they need a large vivarium. Large enough that a good temperature gradient can be maintained (50 degrees hot end 20-25 degrees “cold” end) and that the substrate can be deep enough to remain moist under the surface.
As large an enclosure as possible is desirable but a minimum of 4’x2’x2′. Some people recommend larger to ensure the correct depth of substrate but by using stones to form a retaining wall you can acheive the necessary depth in a vivarium of this size.
Make sure that when being assembled the edges of the vivarium are well sealed. The idea is to have moist soil in the viv and if care is not taken to seal all the edges and joins the vivarium will not last long. Better still use glass, although these are more expensive. Plastic will work well, I just don’t like them myself.
Ackies will make their own burrows but then they are not accessible. Providing a hide will encourage it to stay where you can find it. Providing plenty of hides throughout the enclosure will give the lizard a choice of where to hide when maintaing body temperature so the more the merrier.
A large water bowl is good idea. Placed correctly, overfilling the bowl can help keep the lower levels of substrate moist and the Ackie will certainly relish going in the bowl. Ours burrow under the bowl, which is at the cooler end of the viv. I assume this creates a cooler hide and ours move between this and their “favourite” rock hide during the day
Heating
Ackies like it HOT. My preferred way to create a very hot basking area is with a combination of ceramic heat emmitter (on all the time) and basking lamp (on during the day). In very large vivs you can use a combined heat and UV lamp. These are not dimmable but if the viv is big enough and the lamp sized correctly, as they like it so hot, you can get away with it. You will still need another form of heat for overnight when the lamp is off. If in any doubt, go for a combinination of heat emmiter and basking lamp with a pulse proportional stat on the emmitter. This will give you control day and night.
Lighting
Ackies need high intensity UV. If you have a large viv. and have gone for a combined heat and UV basking lamp then job done. If not, you will need as large a wattage 10% or 12% UVB tube as you can fit in the viv. Fitting a reflector to the tube will greatly increase the amount of UV recieved by the lizard. UVB is essential for calcium metabolism (manufacture of vitamin D3 in the skin) so is not an “optional” requirement.
UVB tubes stop giving out noticeable levels of UV after around 9 months (the combined heat and UV lamps a little longer), so ensure you budget to replace these. Unless you have an expensive UV monitor you will not notice the difference but your lizard will and if the tube is not replaced will eventually get metabolic bone disease and probably die a painful death. If you cannot afford the replacement tubes, don’t get an Ackie.
Basking lamps and UVB lamps should be switched off overnight to give a good day/night cycle. Leaving lighting on all night can stress diurnal animals (and is a waste of electricity and will speed up the replacement of your UVB lamps!). Also, by having a dark rest period they tend to be more acitve during the limited (around 12 hours) daylight hours.
Substrate
Ackies like to dig. They will dig hunting for food, they will dig out burrows to rest in, they will dig to lay eggs, sometimes they will just dig! Therefor the substrate needs to be as deep as you can make it. As already alluded to, you can make a retaining wall with rocks to create an area with deeper substrate. In the wild they like to move around rocky outcrops and drop into gaps when threatened so putting in plenty of areas to climb and hide is a good idea. They will dig out a burrow to hide in and this needs to be at a higher humidity than the surrounding air. To maintain this, regular dampening or misting of the substrate is required to stop it drying out. If it is too shallow, not only will it not support a burrow, it will dry out too quickly. That said the word is damp, not wet!
A good soil, sand mix works well. I like to use desert bedding. It has a good structure that retains moisture at lower levels and can suport burrows without collapse. Other types of soil are also suitable. Mixing in some coir helps moisture retention but I don’t like Ackies on pure coir (has to be too wet to support a burrow)
Feeding
Like other monitors, Ackies are carnivores. The bulk of their diet should be insects but they will take pinkes and fuzzies etc. (although weaned rodents contain more calcium and less fat), as well as a little egg and turkey (I don’t bother with turkey myself) . Don’t use dog and cat food – some people do but it is never a good idea. Ackies store fat in the base of their tails. Feeding to much meat (i.e. food they don’t have to actively hunt) can lead to obesity, although they are nowhere near as prone to this as say, a Bosc Monitor. Better to encourage them to run around hunting by feeding live insects. I use gut loaded cockroaches in the main but vary this as much as possible. We sell livefood so I always have a wide range avaiable so I am a bit spoilt for choice. Dust the food with calcium a few times a week(every day when young) and vitamin powder once a week. Gut loading the insects prior to feeding is the best way to ensure a balanced diet.
Breeding
I am not going to go into detail about breeding. Female Ackies are cyclical breeders. They build up fat stores in their tails and when a certain level is reached and conditions are right, they start to produce eggs. When ready they produce a pheramone that stimulates the male into mating behaviour. Fertilzed eggs are then laid in a burrow. As with most lizards, if the eggs are removed to an incubator for hatching they must not be turned and must be kept in their original orientation or the embryo will die.
Should I get one?
Ackies are great lizards to keep. Most will become quite tame (our male is very tame, the female less so, although she can be handled). They do need large enclosures and the right equipment, regularly maintained. They are probably not for someone who has never owned a reptile before but make a good step up from the usual beaded dragons and leopard geckos etc. Remember they are quite long lived, 15 – 20 years so if considering these fascinating little monitor lizards you need to understand the comittment you are undertaking before buying. They are quite hardy if kept under the right conditions but it is always wise to find out where your nearest specialist reptile vet is located before you need to use one. Normal vets will not have a clue with most reptiles.
The Angell Pets Team









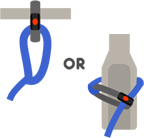 Simply click the Easy-Tie to a café table, railing, post or any other narrow object. Alternatively, you can wrap your lead around a small tree or lamppost, and back on to the lead to create a lock. Features a red lock button for added security.
Simply click the Easy-Tie to a café table, railing, post or any other narrow object. Alternatively, you can wrap your lead around a small tree or lamppost, and back on to the lead to create a lock. Features a red lock button for added security.

